|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
There a 3 states of matter that you need to know about in year 5. Solids, liquids a
|
||||
Gases have the most energy of all the states. Their particles are bouncing all over the places and have no fixed shape or volume.
Move your mouse over the solids, liquids and gases in the picture to see what the particles of water are doing.
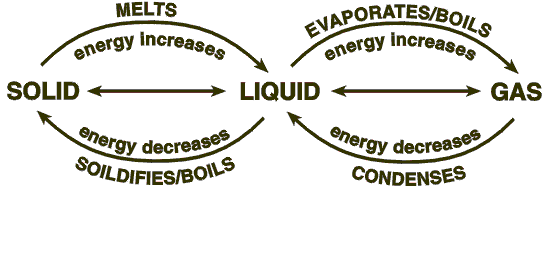
Changing states
Melting
when heat energy is given to a substance the particles vibrate more and more. as a result the temperature increases. When a solid gains enough energy the particles can begin to slide past each other and the solid melts.
Evaporating
As the liquid heats up the particles vibrate even more and begin to break away from the liquid to form a gas. this is called evaporating but it only happens at the surface of a liquid.
The reverse happens when a gas cools.
Condensing
As a gas cools down, the particles lose energy so they begin to form a liquid. this often happens on cold surfaces and is called condensation.
Solidifying
When the particles in a liquid lose energy, they cool down. eventually they have lost so much energy that they clump together as a solid. This is called solidifying.
Interesting facts you need to know:-
The difference between evaporating and boiling.
A substance can begin to evaporate as soon as it is a liquid.
the hotter a liquid is, the quicker it will evaporate. (This is why puddles evaporate quicker on hot days.)
when all the particles in a liquid have enough energy to turn into a gas, the liquid is said to boil.
Solidifying and freezing
If a substance is water or contains water it can be said to freeze. E.g. milk, orange juice etc. All other substances solidify when they go from a liquid to a solid.
Melting points
Pure substances melt at a single temperature. they also freeze or solidify at the same temperature. E.g. water melts at 0°C. Water also freezes at the same temperature.
Softening
Pure substances melt at a set temperature, the melting point. Mixtures melt over a range of temperatures and soften before they melt completely. Examples of these are butter and chocolate. Here is a video all about tempering chocolate so that it melts in your mouth and not in your hand.
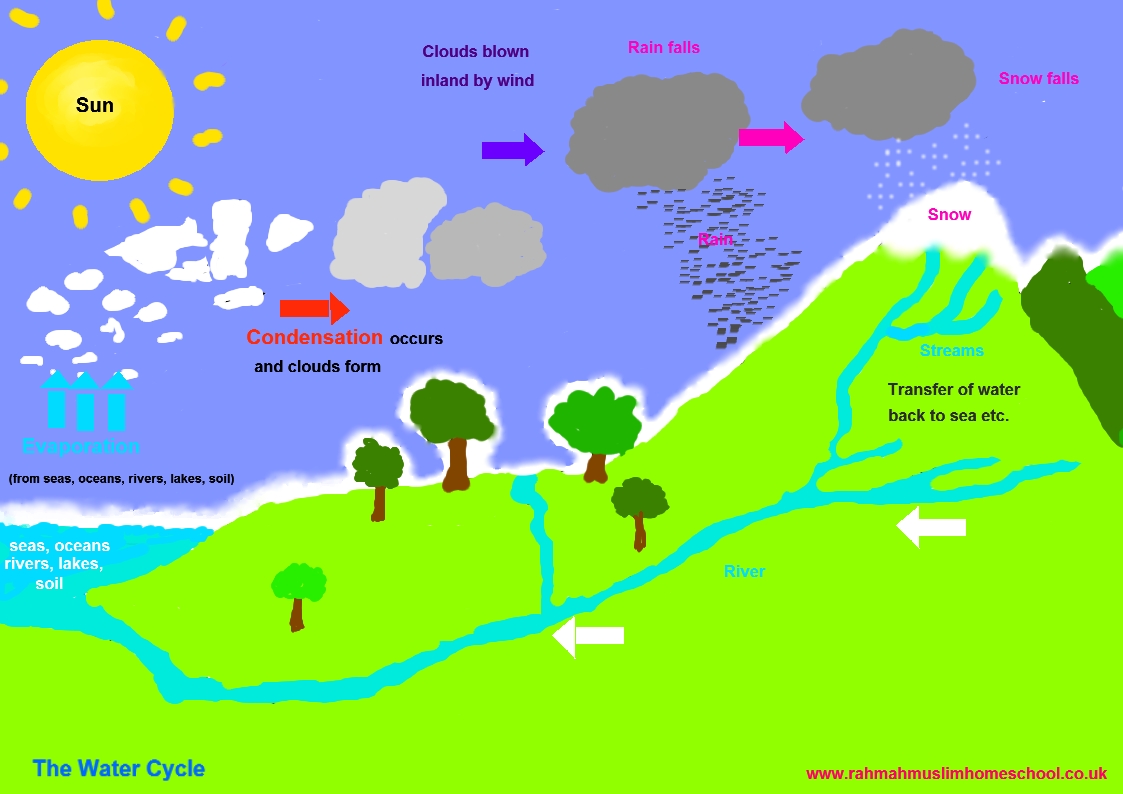
The water cycle is very important to life on earth It also helps us to understand and demonstrate different changes of state in the real world.
Here are a few videos and animations that might help you to better understand the water cycle.![]()
This link might also help you.
![]() This is a fun water cycle song that will help you learn how the water cycle works.
This is a fun water cycle song that will help you learn how the water cycle works.
Soils
There are several different types of soils that are found around the country. Three types are sandy soils, clay soils and loam soils. Different plants prefer different types. Each type also allows different amounts of air to circulate between the particles. this experiment shows how you can find out how much air is in a given amount of soil.
Gases
There are many uses for gases in industry and the home. Here are a few videos that look into this further. Some of the chemistry is a little advanced but do not worry about that this year.
 nd gases.
nd gases.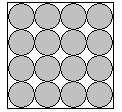 Solids
Solids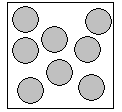 Liquids
Liquids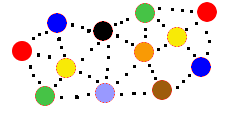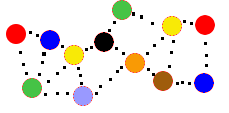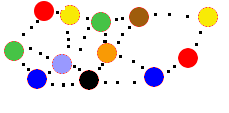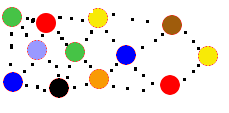
 Gases
Gases